5G Basic PART I
Home LTE NB-IoT 5G(NR-NSA)
References:
1) 3GPP TS 23.501 V15.0.0 system architecture for the 5G system ( stage 2).
Hi guys, this is our first 5G basic part in which we touch upon the difference between gNB and ng-eNB and service based architecture.
What is gNB?
It is the node that provides NR Control Plane and User Plane protocol terminations towards the UE.
gNB is connected to the 5G Core Network through the NG Interface.
What is ng-eNB?
It is the node which provides E-UTRA/LTE Control Plane and User Plane protocol terminations towards the UE.
ng-eNB is connected to the 5G Core Network through the NG Interface.
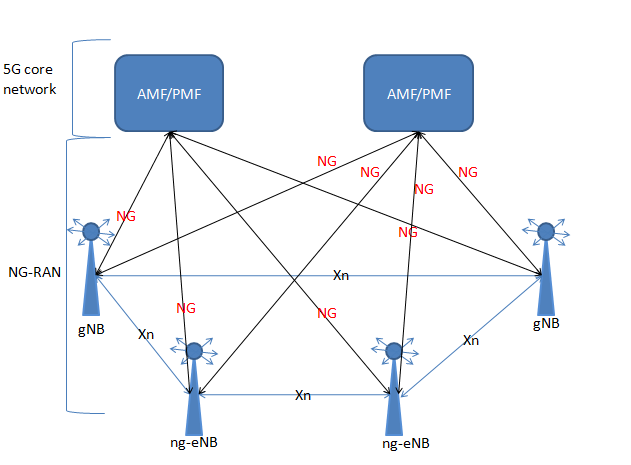
NG-RAN is the representation of the newly defined Radio Access Network(RAN) for 5G.
It allows the UE(device) to get both NR and LTE radio access.
The below diagram shows the inter-relation of NG-RAN with the overall 5G Core Network system.
What is NG-RAN Architecture?
NG-RAN is the representation of the newly defined Radio Access Network(RAN) for 5G.
It allows the UE(device) to get both NR and LTE radio access.
The below diagram shows the inter-relation of NG-RAN with the overall 5G Core Network system.
Xn interface:
An ng-eNB is connected with other ng-eNBs and gNBs through the Xn interface.
NG interface:
It is the interface which connects the ng-eNBs or gNBs with the 5G Core Network.
In the Control Plane, the AMF and ng-eNB/gNB are connected by NG-C interface and in the User Plane, the UPF and ng-eNB/gNB are connected by NG-U interface.
5G System Architecture:
The Network Function services of every Control Plane Function are exposed through the service-based interface:
It also known as 5G system SBA( service based architecture).
The main 5G NFs are the following:
(Note:all functionalities of individual functions are not mentioned)
Network Function
|
Functional
description(supports)
|
AMF
(Access and
Mobility Management function)
(It can be said that AMF has part of MME functionality from legacy LTE EPC.)
|
Access authentication and authorization, Security
context management, Mobility Management, Termination of NAS signaling, Registration Management, Connection management, NAS ciphering & integrity protection
Provide transport for SMS messages between UE and
SMSF (Security Anchor Functionality), Location Services Management for
regulatory services, EPS Bearer ID allocation for inter-working with EPS, UE
mobility event notification, It helps to transport SM messages between UE and
SMF.
|
SMF
(Session
Management function)
(It can be said that SMF has part of the MME and PGW functionality from legacy LTE EPC.)
|
UE
IP address allocation & management, Session Establishment, modify and
release, including tunnel maintain between UPF and AN node, DHCPv4 (server
and client) and DHCPv6 (server and client) functions, Selection and control
of UP function, Configures traffic steering at UPF to route traffic to proper
destination, Termination of interfaces towards Policy control functions, Charging
data collection and support of charging interfaces, Control and coordination
of charging data collection at UPF, down-link Data Notification, Roaming
functionality.
|
UPF
(User plane
function)
(It can be said that UPF has part of the SGW & PGW functionality from legacy LTE EPC.)
|
Anchor point for Intra-/Inter-RAT mobility, External
PDU Session point of interconnect to Data Network, Packet routing &
forwarding, Packet inspection, User Plane part of policy rule enforcement,
e.g. Gating, Redirection, Traffic steering, Lawful intercept (UP collection),
Traffic usage reporting, QoS handling for user plane, Uplink Traffic
verification (SDF to QoS Flow mapping), Transport level packet marking in the
uplink and downlink, Downlink packet buffering and downlink data notification
triggering, ARP proxying.
|
PCF
(Policy Control
Function)
(It can be said that PCF has part of the PCRF functionality from legacy LTE EPC.)
|
Supports
unified policy framework to govern network behavior, Provides policy rules to
Control Plane function(s) to enforce them, Accesses subscription information
relevant for policy decisions in a Unified Data Repository (UDR).
NOTE: The PCF can access the UDR which is located in the same
PLMN as the PCF.
|
NEF
(Network
Exposure Function)
|
It Exposes the capabilities and events, Securely provisions the information from external applications to 3GPP network, Translates internal-external information,
It function is to store the received information in the form of structured data by using a Standardized
interface to a Unified Data Repository (UDR) (interface is to be defined by
3GPP). The stored information can be accessed and "re-exposed" to other network functions and Application Functions by the NEF, and can be used for
other purposes such as analytics.
|
NRF
(Network Repository
Function)
|
Maintains the NF profile of available NF instances
and their supported services, NF instance ID,NF type, PLMN ID, Network Slice
related Identifier(s) e.g. S-NSSAI, NSI ID.
FQDN or IP address of NF,NF capacity information, NF
Specific Service authorization information, Names of supported services, Endpoint
Address(es) of instance(s) of each supported service, Identification of
stored data/information.
For more information please check 3GPP TS 23.501
version 15.2.0 Release 15 6.2.6.
|
UDM
(Unified Data
Management)
|
User identification handling, Support of de-concealment
of privacy-protected subscription identifier, Access authorization based on
subscription data, generation of Authentication and Key Agreement (AKA)
credentials, Support to service/session continuity, Lawful Intercept
Functionality, Subscription management.
|
AUSF
(Authentication
Server Function)
(It can be said that it is a part of HSS
functionality from legacy LTE EPC.)
|
Acts as an
authentication server.
|
AF
(Application
Function)
|
It influences traffic routing, Accessing Network Exposure in Application layer and interacts with the Policy
framework for policy control.
|
NSSF
(Network Slice
Selection Function)
|
Selecting
the set of Network Slice instances serving the UE, Determining the Allowed
and Configured NSSAI and, if needed, the mapping to the Subscribed S-NSSAIs, Determining
the AMF Set to be used to serve the UE, or a list of
candidate AMF(s) (based on configuration) possibly by querying the NRF.
|
References:
1) 3GPP TS 23.501 V15.0.0 system architecture for the 5G system ( stage 2).





SMF
ReplyDelete(Session Management function)
(It can be said that SMF has part of the MME and PGW functionality from legacy LTE EPC.)
But I believe, that SMF is a part of MME and SGW-C functionality from legacy LTE EPC.
Correct me, if i am wrong..